Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a key environmental protection policy instrument that encompasses and influences a wide variety of areas related to the environment, including the impact of proposed activities on the landscape.
Assessing the impact of potential changes on the landscape and cultural-historical objects is a complex task. It requires an in-depth understanding of existing regulatory frameworks and planning documents, surveying the area, assessing the impact of planned activities, modeling various scenarios, and providing recommendations.
Jāņa sēta offers to conduct a landscape impact assessment, ensuring a comprehensive analysis of the planned object’s impact. Our assessments include both qualitative and quantitative analyses, leveraging our team’s extensive experience, geographical knowledge, available geospatial data, and expertise in performing geospatial analyses using data from various sources.
Stages of the Landscape Impact Assessment
- Qualitative Approach
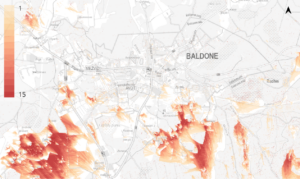
In the assessment process, the area is surveyed on-site, with special attention given to significant locations such as cultural-historical and tourism sites, densely populated areas, and particularly valuable viewpoints.
A critical aspect of the assessment is analyzing existing planning documents, focusing on landscape values mentioned in these plans and the compatibility of the proposed activity with these documents, while also considering international experience in landscape impact assessments for similar projects.
Unconventional data sources, such as human movement data in potentially affected areas, are also evaluated.
- Quantitative Approach
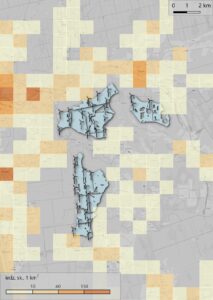
To evaluate the concept of the planned activity, it is important to conduct a quantitative analysis that assesses the visual impact of the object on the landscape. This is especially crucial for the impact assessment of wind power stations (WPS), as the visibility distance of these objects can exceed 10 kilometers. In the landscape assessment process, we perform calculations to identify visibility zones around the planned object and assess the population density in the area surrounding the proposed activity.
- 3D Modeling and Visualization Development
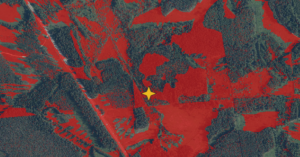
Using GIS solutions, we accurately model how the planned objects will integrate into the landscape. We use precise surface models of the earth to simulate the visibility of specific turbines from surrounding areas. We utilize the latest data on land vegetation and can also model its near-future changes.
- Documentation development, recommendations
The work of landscape experts and GIS specialists is summarized in a landscape impact assessment report. The report compiles all the conclusions drawn from the conducted assessment and includes modeled views from the most significant viewpoints. The report also contains recommendations for changes in the location or technical parameters of specific objects, or for other measures to mitigate the impact.
Examples